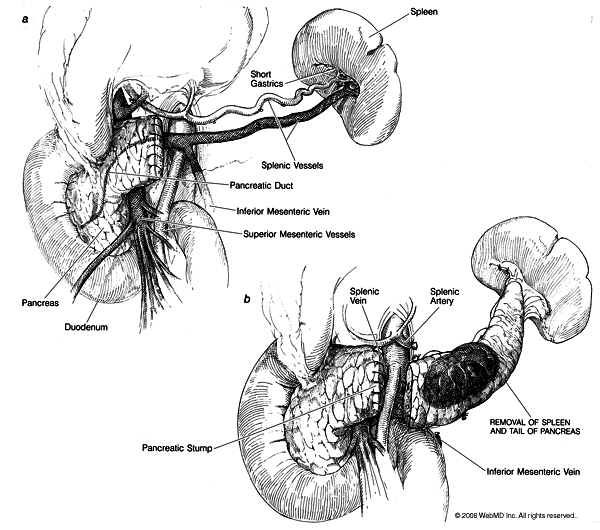
Left pancreatectomy
Left (or distal) pancreatectomy is performed to treat pancreatic diseases of the tail and body. This operation involves surgical resection of the body and tail of the pancreas to the left of the superior mesenteric-portal vein confluence. Left pancreatectomy can be carried out with or without associated splenectomy. The choice of procedure depends upon the disease process, and the characteristics of the lesion.
- Left pancreatectomy with splenectomy: The spleen, which is located near this part of the pancreas and shares some of the same blood vessels, needs to be removed as part of the procedure when the underlying pancreatic neoplasm is aggressive. Left pancreatectomy with splenectomy enables ligation of splenic vessels at their origin and an adequate lymph node clearance (Figure).
- Spleen-preserving left pancreatectomy: This procedure is reserved for benign/borderline pancreatic lesions and cysts, and for localized neuroendocrine tumors. There are two distinct approaches to preserve the spleen during the dissection of the distal pancreas. The classic design is to identify, isolate, and preserve the splenic artery and vein (Kimura procedure). Alternatively, the splenic artery and vein are ligated with the pancreas, and perfusion of the spleen is assured by the short gastric vessels (Warshaw procedure). Both are accepted as appropriate techniques to address a mass in the tail of the pancreas.
The pancreatic stump can be either hand-sutured, closed with a stapler, or sealed with harmonic scalpel. These stump closure techniques seem to be equivalent.
Minimally invasive surgery is becoming the paradigm in left pancreatic resections (laparoscopic and robot-assisted left pancreatectomy). In the next future, the number of left pancreatic resection performed with minimally invasive techniques is likely to increase due to a variety of factors including increased operator experience across centres and acceptance of the technique on the basis of demonstrated outcomes in premalignant and malignant lesions. For more information on the minimally invasive pancreatic surgery click here.