Minimally invasive surgery
Minimally invasive surgery is performed through small incisions, usually between 5-15 mm. The surgeon then inserts specially designed, thin instruments and sophisticated video equipment to perform the operation through the smaller opening. Depending on the procedure, minimally invasive surgery can be performed with the surgeon manipulating the instruments by hand (laparoscopic surgery) or with the surgeon directing robotic arms (robot-assisted surgery).
Minimally invasive surgery offers many benefits over traditional techniques, including less injury to tissue, less postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, quicker return to normal activities, minimal scarring, less incisional hernias. Over the past 20 years minimally invasive surgery has evolved to such an extent that in suitably qualified hands the majority of general surgical procedures can be safely carried out.
The complexity of pancreatic surgery has meant that the development of laparoscopic techniques and particularly formal resections has been relatively slow compared with procedures in many other surgical specialties. Consequently its incorporation into regular clinical practice is recent, and initial indications were limited to benign and borderline neoplasms. Recent data indicate that laparoscopic pancreatic resections are oncologically adequate, and can be safely applied to malignant neoplasms. The most commonly performed laparoscopic pancreatic resections are left pancreatectomy and enucleation.
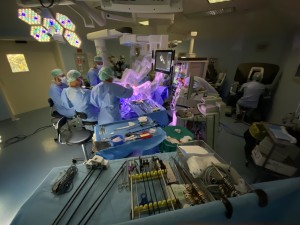
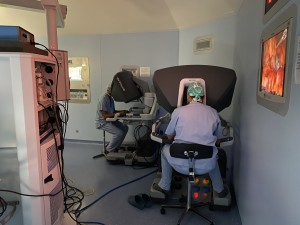
Miimally invasive surgery has been further enhanced by the use of robotics. Robotic surgery is a technique in which a surgeon performs surgery using a computer that remotely controls very small instruments attached to a robot. With the surgeon sitting at a console a few metres from the patient, the robot translates that surgeon’s hand movements into corresponding micro-movements of instruments inside the patient’s body. The robotic system provides better visualization, dexterity, precision and control than open surgery, while enabling the surgeon to perform procedures through tiny, 1-2 cm incisions. The world experience on the use of robotic systems for surgery on the pancreas is growing, but remains limited to very experienced centers.
The Unit of Pancreatic Surgery in Verona has one of the largest minimally invasive practice in Italy. Our program has a history of pioneering innovative, minimally invasive approaches for pancreatic neoplasms. We have developed experience with the da Vinci Xi HD robotic system for all types of pancreatic resections, left pancreatectomy, with or without splenectomy, pancreatoduodenectomy, total pancreatectomy, middle pancreatectomy, and enucleation.